 recognition:(MICR)
recognition:(MICR)MICR is a character recognition technology used primarily by the banking industry to facilitate the processing of cheques. The technology allows computers to read information (such as account numbers) off of printed documents. Unlike barcodes or similar technologies, however, MICR codes can be easily read by humans.MICR characters are printed in special typefaces with a magnetic ink or toner, usually containing iron oxide. As a machine decodes the MICR text, it first magnetizes the characters in the plane of the paper. Then the characters are then passed over a MICR read head, a device similar to the playback head of a tape recorder. As each character passes over the head it produces a unique waveform that can be easily identified by the system.
Optical character:(OCR)
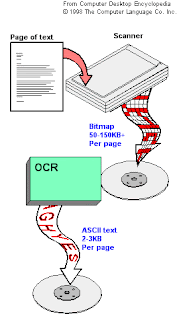
Optical character is the mechanical or electronic translation of images of handwritten, typewritten or printed text into machine text.OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intelligence and computer vision. Though academic research in the field continues, the focus on OCR has shifted to implementation of proven techniques. Optical character recognition and digital character recognition were originally considered separate fields. Because very few applications survive that use true optical techniques, the OCR term has now been broadened to include digital image processing as well.
Optical mark recognition:(OMR)
recognition:(OMR)
Often abbreviated OCR, optical character recognition refers to the branch of computer science that involves reading text from paper and translating the images into a form that the computer can manipulate. An OCR system enables you to take a book or a magazine article, feed it directly into an electronic computer file, and then edit the file using a word processor. All OCR systems include an optical scanner for reading text, and sophisticated software for analyzing images. Most OCR systems use a combination of hardware and software to recognize characters, although some inexpensive systems do it entirely through software.
Dot matrix printer:
A dot matrix

printer or impact matrix printer is a type of computer printer with a print head that runs back and forth, or in an up and down motion, on the page and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper, much like a typewriter. Unlike a typewriter or daisy wheel printer, letters are drawn out of a dot matrix, and thus, varied fonts and arbitrary graphics can be produced. Because the printing involves mechanical pressure, these printers can create carbon copies and carbonless copies.
Plotter:
plotter is a dev

ice that draws pictures on paper based on commands from a computer. Plotters differ from printers in that they draw lines using a pen. As a result, they can produce continuous lines, whereas printers can only simulate lines by printing a closely spaced series of dots. Multicolor plotters use different-colored pens to draw different colors.
In general, plotters are considerably more expensive than printers. They are used in engineering applications where precision is mandatory.
PHoto printer:
printers cu

rrently sold to home users are marketed as "photo printers" because there are no official specifications designating what is and isn't a photo printer. Not all these models print photos as well as dedicated photo printers can, so some see this as a marketing ploy to increase the appeal of the product to the consumer.
Portable printer:
portable print

ers provide workers with the ability to print documents while on the road. Usingportable printers can save time and allow you to be more productive. Find out what different portable printers offer and which mobile printers is best for your needs.
Fax machine:
Fax is a teleco

mmunications technology used to transfer copies of documents, especially using affordable devices operating over the telephone network. The word telefax, short for telefacsimile, for "make a copy at a distance", is also used as a synonym. Although fax is not an acronym (as it is abbreviated from facsimile), it is often written as “FAX”. The device is also known as a telecopier in certain industries.
Multifunctional device: Multifunctional dev

ices bring the worlds of copying, printing, finishing, and scanning together, all in one neat, efficient and cost-effective package. Uniquely, Officemagic has excellent deals on mutifunctional devices specially selected, cutting-edge colour enabled systems. If you thought your company couldn't afford the latest technology - and the huge productivity benefits they offer- it's time to think again. We have low cost, highly efficient black-only multifunctional devices as well as a huge range of colour multifunctional devices to meet your particular requirements.
INternet telephones:
Internet telephon

es is a general term for a family of transmission technologies for delivery of voice communications over IP networks such as the Internet or other packet-switched networks. Other terms frequently encountered and synonymous with VoIP are IP telephony, Internet telephony, voice over broadband , broadband telephony, and broadband phone.
Internet telephony refers to communications services. The basic steps involved in originating an Internet telephone call are conversion of the analog voice signal to digital format and compression/translation of the signal into Internet protocol packets for transmission over the Interne.
 e is a mechanism for improving the time it takes to read from or write to a hard disk. Today, the disk cache is usually included as part of the hard disk. A disk cache can also be a specified portion of random access memory (RAM).The disk cache holds data that has recently been read and, in some cases, adjacent data areas that are likely to be accessed next. Write caching is also provided with some disk caches.
e is a mechanism for improving the time it takes to read from or write to a hard disk. Today, the disk cache is usually included as part of the hard disk. A disk cache can also be a specified portion of random access memory (RAM).The disk cache holds data that has recently been read and, in some cases, adjacent data areas that are likely to be accessed next. Write caching is also provided with some disk caches. e is a mechanism for improving the time it takes to read from or write to a hard disk. Today, the disk cache is usually included as part of the hard disk. A disk cache can also be a specified portion of random access memory (RAM).The disk cache holds data that has recently been read and, in some cases, adjacent data areas that are likely to be accessed next. Write caching is also provided with some disk caches.
e is a mechanism for improving the time it takes to read from or write to a hard disk. Today, the disk cache is usually included as part of the hard disk. A disk cache can also be a specified portion of random access memory (RAM).The disk cache holds data that has recently been read and, in some cases, adjacent data areas that are likely to be accessed next. Write caching is also provided with some disk caches. lowed computer users to achieve high levels of storage reliability from low-cost and less reliable PC-class disk-drive components, via the technique of arranging the devices into arrays for redundancy.
lowed computer users to achieve high levels of storage reliability from low-cost and less reliable PC-class disk-drive components, via the technique of arranging the devices into arrays for redundancy. lowed computer users to achieve high levels of storage reliability from low-cost and less reliable PC-class disk-drive components, via the technique of arranging the devices into arrays for redundancy.
lowed computer users to achieve high levels of storage reliability from low-cost and less reliable PC-class disk-drive components, via the technique of arranging the devices into arrays for redundancy. l because it helps reduce the consumption of expensive resources, such as hard disk space or transmission bandwidth. On the downside, compressed data must be decompressed to be used, and this extra processing may be detrimental to some applications. For instance, a compression scheme for video may require expensive hardware for the video to be decompressed fast enough to be viewed as it's being decompressed (the option of decompressing the video in full before watching it may be inconvenient, and requires storage space for the decompressed video).
l because it helps reduce the consumption of expensive resources, such as hard disk space or transmission bandwidth. On the downside, compressed data must be decompressed to be used, and this extra processing may be detrimental to some applications. For instance, a compression scheme for video may require expensive hardware for the video to be decompressed fast enough to be viewed as it's being decompressed (the option of decompressing the video in full before watching it may be inconvenient, and requires storage space for the decompressed video). l because it helps reduce the consumption of expensive resources, such as hard disk space or transmission bandwidth. On the downside, compressed data must be decompressed to be used, and this extra processing may be detrimental to some applications. For instance, a compression scheme for video may require expensive hardware for the video to be decompressed fast enough to be viewed as it's being decompressed (the option of decompressing the video in full before watching it may be inconvenient, and requires storage space for the decompressed video).
l because it helps reduce the consumption of expensive resources, such as hard disk space or transmission bandwidth. On the downside, compressed data must be decompressed to be used, and this extra processing may be detrimental to some applications. For instance, a compression scheme for video may require expensive hardware for the video to be decompressed fast enough to be viewed as it's being decompressed (the option of decompressing the video in full before watching it may be inconvenient, and requires storage space for the decompressed video).










 A network interface controller (NIC) is a hardware device that handles an interface to a computer network and allows a network-capable device to access that network. The NIC has a ROM chip that contains a unique number, the multiple access control (MAC) Address that is permanent. Sometimes the words 'controller' and 'card' are used interchangeably when talking about networking because the most common NIC is the network interface card. Although 'card' is more commonly used, it is less encompassing. The 'controller' may take the form of a network card that is installed inside a computer, or it may refer to an embedded component as part of a computer motherboard, a router, expansion card, printer interface or a USB device.
A network interface controller (NIC) is a hardware device that handles an interface to a computer network and allows a network-capable device to access that network. The NIC has a ROM chip that contains a unique number, the multiple access control (MAC) Address that is permanent. Sometimes the words 'controller' and 'card' are used interchangeably when talking about networking because the most common NIC is the network interface card. Although 'card' is more commonly used, it is less encompassing. The 'controller' may take the form of a network card that is installed inside a computer, or it may refer to an embedded component as part of a computer motherboard, a router, expansion card, printer interface or a USB device. A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations. As long as most memory accesses are cached memory locations, the average latency of memory accesses will be closer to the cache latency than to the latency of main memory.When the processor needs to read from or write to a location in main memory, it first checks whether a copy of that data is in the cache. If so, the processor immediately reads from or writes to the cache, which is much faster than reading from or writing to main memory.
A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations. As long as most memory accesses are cached memory locations, the average latency of memory accesses will be closer to the cache latency than to the latency of main memory.When the processor needs to read from or write to a location in main memory, it first checks whether a copy of that data is in the cache. If so, the processor immediately reads from or writes to the cache, which is much faster than reading from or writing to main memory. Plug and Play is a set of networking protocols promulgated by the UPnP Forum. The goals of UPnP are to allow devices to connect seamlessly and to simplify the implementation of networks in the home data sharing, communications, and entertainment and in corporate environments for simplified installation of computer components. UPnP devices are "plug-and-play" in that when connected to a network they automatically announce their network address and supported device and services types, enabling clients that recognize those types to immediately begin using the device.
Plug and Play is a set of networking protocols promulgated by the UPnP Forum. The goals of UPnP are to allow devices to connect seamlessly and to simplify the implementation of networks in the home data sharing, communications, and entertainment and in corporate environments for simplified installation of computer components. UPnP devices are "plug-and-play" in that when connected to a network they automatically announce their network address and supported device and services types, enabling clients that recognize those types to immediately begin using the device.



 Personal computers have various types of ports. Internally, there are several ports for connecting disk drives, display screens, and keyboards. Externally, personal computers have ports for connecting modems, printers, mice, and other peripheral devices.
Personal computers have various types of ports. Internally, there are several ports for connecting disk drives, display screens, and keyboards. Externally, personal computers have ports for connecting modems, printers, mice, and other peripheral devices.













 system analyst is responsible for researching, planning, coordinating and recommending software and system choices to meet an organization's business requirements. The systems analyst plays a vital role in the systems development process. A successful systems analyst must acquire four skills: analytical, technical, managerial, and interpersonal. Analytical skills enable systems analysts to understand the organization and its functions, which helps him/her to identify opportunities and to analyze and solve problems. Technical skills help systems analysts understand the potential and the limitations of information technology. The systems analyst must be able to work with various programming languages, operating systems, and computer hardware platforms. Management skills help systems analysts manage projects, resources, risk, and change. Interpersonal skills help systems analysts work with end users as well as with analysts, programmers, and other systems professionals.
system analyst is responsible for researching, planning, coordinating and recommending software and system choices to meet an organization's business requirements. The systems analyst plays a vital role in the systems development process. A successful systems analyst must acquire four skills: analytical, technical, managerial, and interpersonal. Analytical skills enable systems analysts to understand the organization and its functions, which helps him/her to identify opportunities and to analyze and solve problems. Technical skills help systems analysts understand the potential and the limitations of information technology. The systems analyst must be able to work with various programming languages, operating systems, and computer hardware platforms. Management skills help systems analysts manage projects, resources, risk, and change. Interpersonal skills help systems analysts work with end users as well as with analysts, programmers, and other systems professionals.